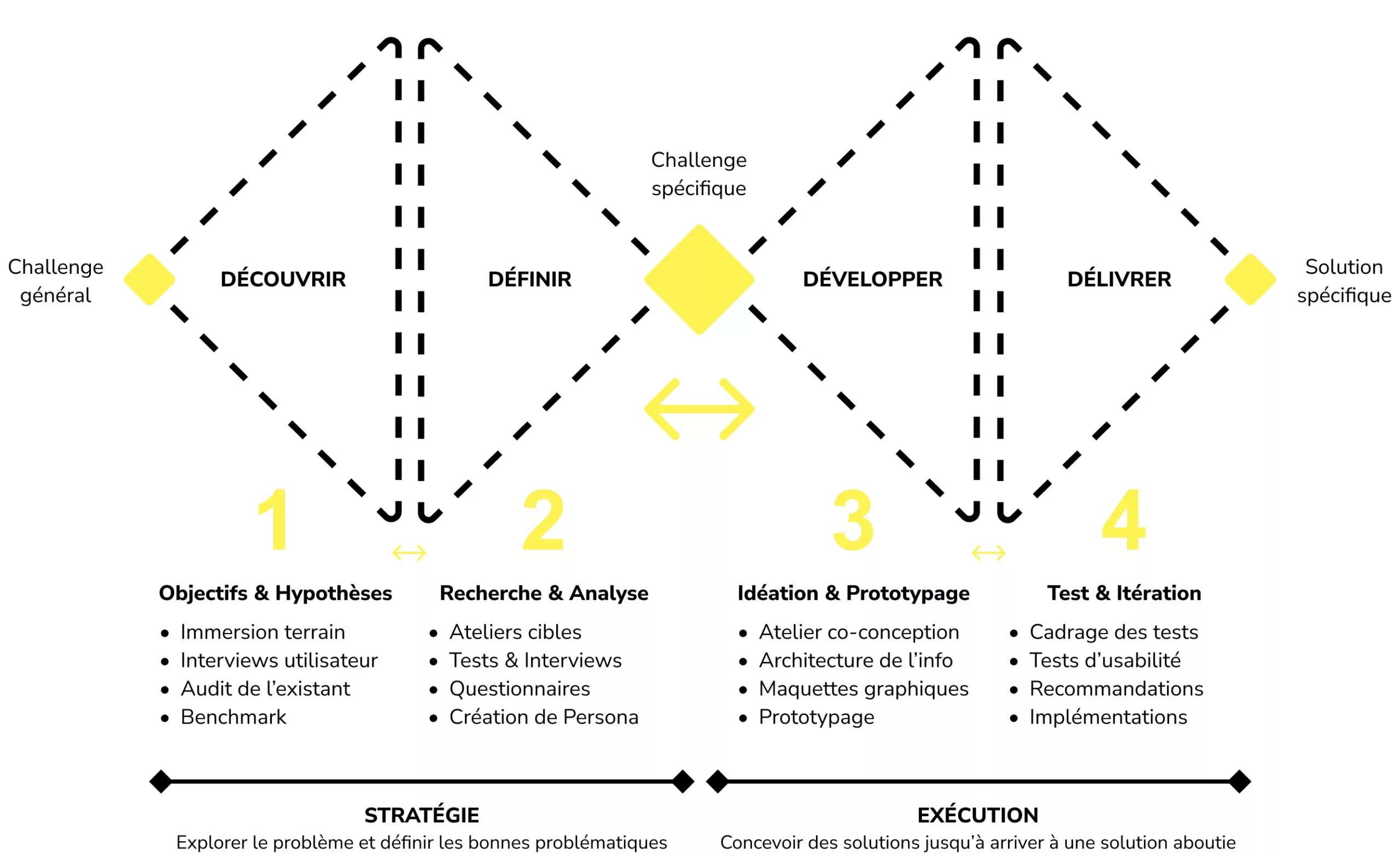
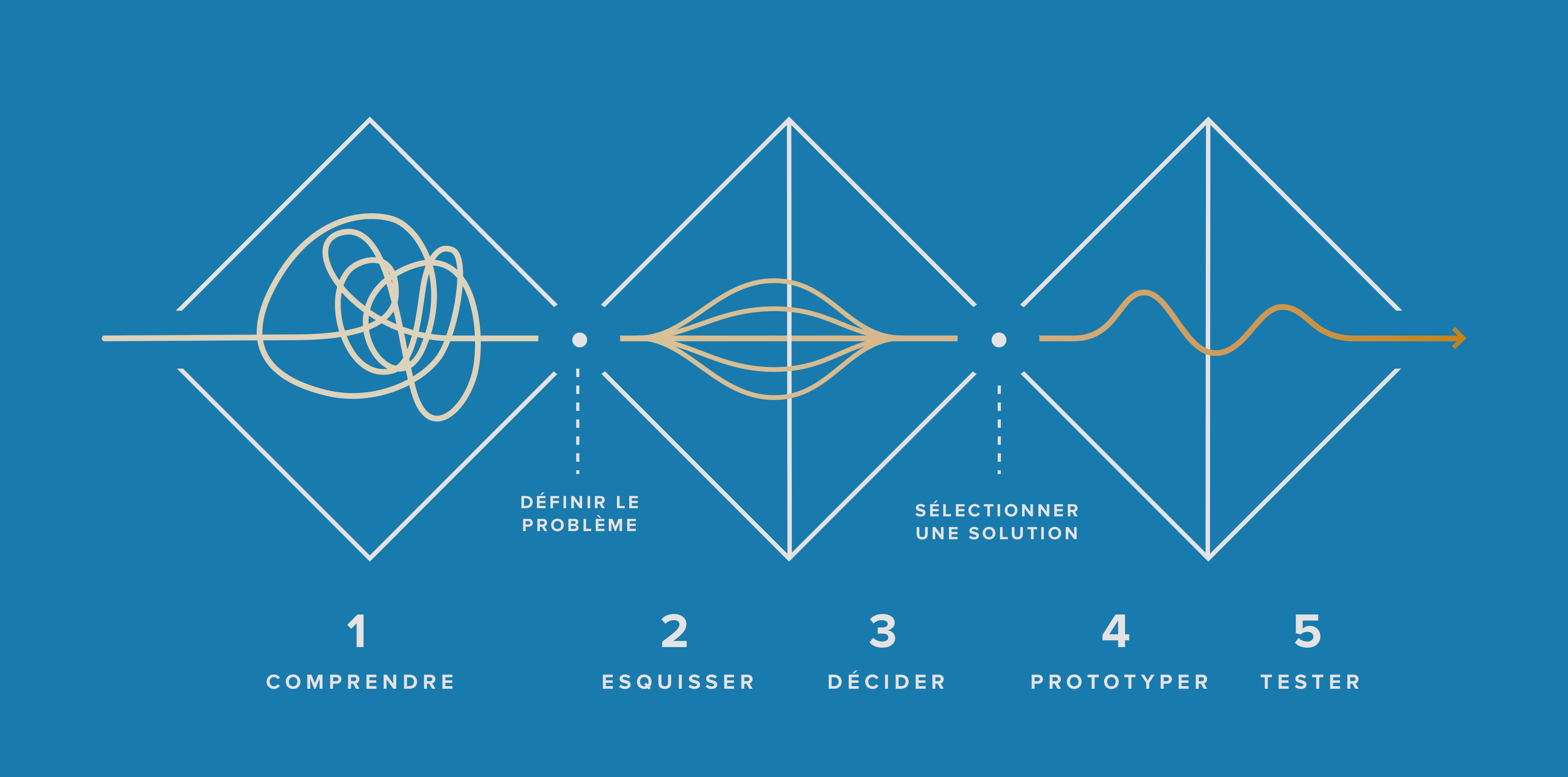
Definition
UX Design (User Experience Design) is a discipline focused on designing products or services with the user at the center of the process. This includes understanding user needs, creating intuitive solutions, and continuously improving based on feedback.
See Details


. La scène montre un groupe diversifié de personnes collaborant autour d'une g.webp)